Brinjal Plant Care: Easy to Grow Tasty Vegetable Plant

Image by usmanzahoor from Pixabay
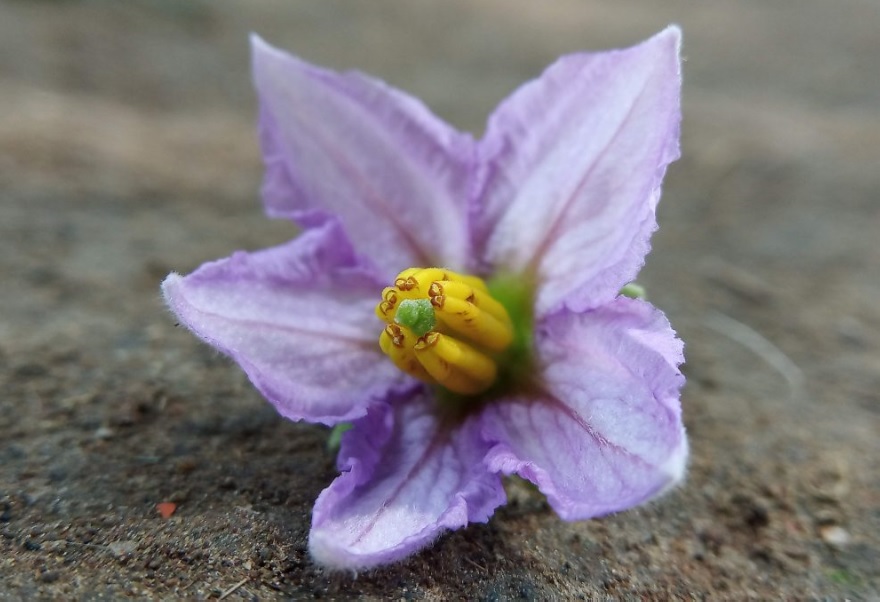
Brinjal or eggplant is one of the popular vegetables used in most parts of the world. It is an easy-to-grow plant. Brinjal plant care is very easy and requires very maintenance if grown in the right condition. The plants with their purple flowers and fruits add beauty to the garden.
Quick Details of Brinjal Plant Care
| Other Common Names | Aubergine, Eggplant, Brinjal |
| Type | Annual/ perennial vegetable plant |
| Maintenance | Low – Moderate |
| Flowering | Spring-Summer |
| Light | Bright direct sunlight for at least 6-8 hours. |
| Water | Regular watering |
| Temperature | Warm climatic conditions |
| Soil | Well draining nutrient rich potting mix |
| Fertilizer | Any organic fertilizer, phosphorous-rich fertilizers |
| Habitat | Temperate and Tropical region |
| Toxicity | The fruit can be allergic to few |
| Common Diseases | Flea beetles, powdery mildew, Aphids, spider mites |
| Scientific name | Solanum melongena |
Brinjal Plant Buying Instructions
- Buy healthy seedlings
- Buy the seedlings which do not have any patches on the leaves.
- You can even purchase seeds of Brinjal but buy seeds of good quality/ brand for better results.
Overview of Brinjal Plant Care
The brinjal plant is a hardy annual or perennial plant grown in tropical and temperate regions. They belong to the Solanaceae family. The fruit is used as a vegetable and is one of the most loved vegetables all around the world. The fruits are primarily long, slender, or egg-shaped and violet in color. Some of the varieties give white fruits as well. The plants flower mostly during the spring-summer season.
The stems have small hairy spines. The leaves are large, with irregular margins. The plants can grow up to a height of 4 feet tall. The fruits are fleshy or spongy in texture with small seeds inside.
The fruits are used as a part of different cuisines all around the world. The fruits are rich in iron, fiber, and calcium and have a low amount of fat.
Usage and Advantage of Brinjal Plant
- The fruit is used as a vegetable.
General Brinjal Plant Care
Soil
Brinjal is an easy-to-grow plant and can be grown in any kind of well-draining potting mix. They grow best in well-draining sandy loamy soil with a pH range of 5.8- 6.5 with high organic content.
Water
Water the plants regularly. They require moist soil. Make sure there is no water clogging or excess water as this can cause root rot.
Sunlight
They prefer bright direct sunlight. Place the plants in spots where they can receive bright direct sunlight for at least 6-8 hours a day.
Temperature
The plants prefer warm conditions with normal humidity. Excess heat or cold can cause stress to the plant and can affect the pollination process and formation of fruits.
Special – Brinjal Plant Care
Brinjal plant care evolves providing just the right conditions. They are hardy and do not require much care. Mulch the soil to prevent excess moisture loss from the soil. They are self-pollinating plants, it is advised to check for proper pollination taking place. In case of lack of formation of fruits, hand pollinates the flowers.
Fertilization
They are heavy feeders and require nutrient-rich soil. Lack of enough nourishment can affect fruit formation. Add an all-purpose fertilizer while planting the seedling or the seed. Feed the plants with a diluted liquid fertilizer or 1/4 of the suggested amount of fertilizer every alternate week. organic manure or vermicompost can also be added. Avoid overfeeding the plant.
Pests and other problems for Brinjal Plant
Some of the common problems faced by brinjal are:
Alternaria Leaf Spots
It is a fungal disease caused by the pathogen Alternaria melongenae. The pathogen infects the leaf and produces concentric rings that are irregular in shape. These rings spread and cause the leaves to wilt and dry. They can also infect the fruits causing large deep spots on them The infected fruits can also turn yellow and fall off even before maturing completely.
In case of any signs of infection, remove the infected part of the plant immediately. Use any mild fungicide or neem oil to get rid of the pathogens at the initial stage of the infection.
Bacterial wilt
It is a bacterial disease caused by the pathogen Pseudomonas solanacearum. The infected part of the plant especially the leaves, turn yellow, wilt, and die. They can spread quickly to the other parts of the plant leading to the death of the plant. The lower leaves start to wilt first, and brown coloration can be seen in the veins of the leaves. In some cases, a liquid starts to ooze out from the infected plant part. The drooping leaves may recover by night but the plant will wilt and die.
Remove the infected part of the plant as soon as possible. A mild fungicide or pesticide can be sprayed to control the spread of the disease. Keep the soil clean and the plants safe from pest attacks.
Blossom-end rot
It is a physiological disorder caused due to a deficiency in calcium or excess nitrogen in the soil. This results in the development of the vegetative part suppressing the growth of the fruit. The fruits develop small water-soaked areas that enlarge and turn sunken. The fruits become leathery and hard.
This is one of the problems caused due to over-fertilization. Make sure to provide enough nourishment to the plant. Avoid over-fertilization.
Little Leaf of Brinjal
It is a viral disease transmitted by the insect Cestius physics (Leaf hopper) The infected leaves turn yellow, and starts to reduce in size and looks distorted. The infected plants have stunted growth, with numerous branching than normal plants. The plants are short and bushy. The flowers can also be deformed and hence no fruits are formed.
Remove the infected plants as soon as possible as there is no cure for this viral infection and it spread quickly in the plant and from one plant to another. Spray pesticides or neem oil to keep the vector insects at bay.
Brinjal flower drop
There are multiple following factors that can be a reason for flowers not turning into fruits:
- Lack of nutrients
- Watering issues
- Temperature
- Lack of pollination – How to treat brinjal flower pollination issue
Read more about Brinjal Flower Drop Control
Propagation of Brinjal Plant
It is an easy-to-grow plant and the propagation in brinjal plants takes place through seeds. The seeds can either be bought directly from the nursery or can be saved from the fruits already growing in the garden. Allow the fruits to stay in the plant till it either gets harder and lose their color or become mushy. The seeds can be scooped out washed and dried.
These seeds can be further germinated directly into the soil or into germinating bags or pots containing any organic potting mix till the seedlings start to appear. Water the pots regularly and ensure they are placed at optimum temperature (around 25-29 degree Celsius). Once the seedling appears, transplant them into bigger pots or directly into the soil.
FaQ:-
The color of the Brinjal flower is violet.
One of the main reasons for the falling of Brinjal flowers is the lack of adequate water. They also fall if pollination has not occurred.
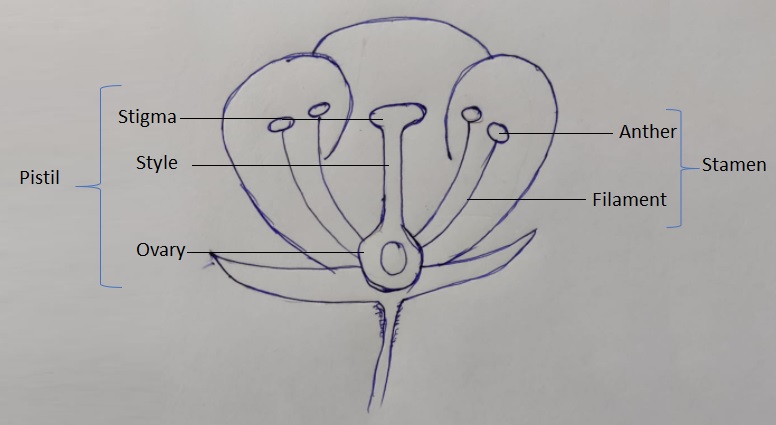
Based on the length of the Brinjal flower’s style, the flowers are classified into four varieties – (1) Long style and large ovary, (2) Medium style and medium style, (3) Pseudo style and underdeveloped ovary, and (4) True short style and primitive ovary. Long and medium-style Brinjal flowers are fruit-setting flowers. The fruit setting of long-style flowers ranges from 70 to 80% and medium-style from 12 to 55%.
The Brinjal flower is a self-pollinating flower and also has cross-pollinating characteristics. They self-pollinate through vibration induced by air and rain and through hand-shaking. Bumblebees and various insects are pollinating agents of cross-pollination of the Brinjal flower.
Long and medium-style Brinjal flowers are fruit-setting flowers. The fruit setting of long-style flowers ranges from 70 to 80% and medium style from 12 to 55%.